beginner
Polygon, previously known as Matic network, is a well-established cryptocurrency that is well-recognized among crypto investors and enthusiasts. However, not as many people know that it is actually a layer 2 solution to another digital asset — Ethereum.
Why is that important, you may ask? Well, for one, it makes this cryptocurrency more future-proof. According to the creator of Ethereum, Vitalik Buterin, many post-Merge improvements to the main network will be done using layer 2 solutions like Polygon.
Polygon does more than just make the Ethereum ecosystem more efficient — it enables cross-chain communications for different blockchains in the network. It is also one of the best platforms for creating interconnected blockchain networks. Polygon’s team refers to their project as “Ethereum’s Internet of blockchains.”
Who Сreated Polygon?
Polygon was created in October 2017 by India’s first crypto billionaires: Jaynti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal, and Anurag Arjun. Back then, it was known as the “Matic network.”
The Polygon ecosystem has always been envisioned as an “assistant” to the Ethereum network, aiming to solve and address its key issues, such as high gas fees and lack of proper scalability solutions. Despite that, it does have its own independent proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain.

The Founders of Polygon
Jaynti Kanani, the CEO of Polygon, has a background in software engineering. He had worked at companies like Microsoft, Amazon, and Adobe in the past.
Anurag Arjun, the CTO of Polygon, is a polymath who has experience in fields like machine learning, mathematics, and physics.
Sandeep Nailwal, the COO of Polygon, has over 15 years of experience in the financial sector. He previously worked at Deloitte as a management consultant. Nailwal is also the co-founder of Aave, another popular cryptocurrency project.
Polygon’s Rebranding
In 2021, the team behind Polygon decided to rebrand the project in order to better reflect their vision of a polychain scaling platform that supports multiple blockchains. The new name, Polygon, was chosen because it channels the idea of a “network of many different chains.”
In addition to changing the network’s name, new features also got introduced, elevating Polygon above its previous status as a simple scaling solution that could only offer plasma chains.
This rebranding has been an immense help in increasing awareness of Polygon and its native token, MATIC. The new name clarified what the network intended to do and brought much attention to this cryptocurrency.
What Is the MATIC Token?
The native token of the Polygon network, MATIC is used to pay transaction fees and can also be staked in order to earn rewards for helping to secure the network. In addition, developers who build on Polygon can use MATIC tokens to access features like gas-free withdrawals and fast transactions.
You can buy MATIC token on Changelly.
How Does Polygon Work?
The Ethereum blockchain undeniably has a lot of issues that gravely impede its growth. Slow transaction speeds and high gas fees make it impossible to use ETH for everyday payments. Polygon allows users to carry out those same Ether transactions but in a faster, cheaper, and overall much more efficient way.
To do this, Polygon uses a modified proof-of-stake algorithm to secure its network, thus making it possible for consensus to be reached with every single block. The Polygon network is made up of a series of sidechains connected to the Ethereum mainnet. These sidechains are used to process transactions off-chain, which helps improve the network’s scalability.
Let’s take a look at some of the principal characteristics of the Polygon network.
Layer 2 Solution
Polygon is a layer 2 solution that helps to scale the Ethereum blockchain. It does this by using sidechains connected to the main Ethereum blockchain. This allows for off-chain transactions that are then settled on-chain. Another perk here is that it enables Polygon to process transactions much faster than ETH.
Developers who build on Polygon can use MATIC tokens to pay transaction fees. Thanks to this, Polygon has lower transaction fees than Ethereum. In addition, Polygon has implemented a number of features to reduce gas costs, such as gas-free withdrawals and fast transactions.
Later 2 solutions are going to play a key role in Ethereum’s development after the Merge. As a result, more and more people will likely become aware of this amazingly innovative technology and, by extension, Polygon.
Proof of Stake (PoS)
Having a PoS blockchain allows Polygon to take advantage of features like smart contracts, which enables the creation and deployment of decentralized applications (dApps). Additionally, it lets users who hold MATIC tokens stake them to earn rewards. This makes the network attractive to developers and investors alike.
Polygon’s team also used the proof-of-stake nature of its consensus mechanism to implement a number of security features, such as fraud proofs.
Polygon Bridge
The “Polygon Bridge” is the solution that allows Polygon to connect to the Ethereum network. It also enables the transfer of NFTs and ERC-20 tokens from the MATIC blockchain to the ETH one.
Polygon has two main bridges: the Proof-of-Stake and the Plasma Bridge. Although both of them have the same purpose — transferring digital assets from one blockchain to another — they employ different security methods.
Just like the name suggests, the proof-of-stake bridge uses the PoS consensus mechanism as its primary security measure. It is what helps most investors and dApp users to transfer tokens and ETH between the two chains. The Plasma bridge is more popular with developers as it is generally more secure. However, plasma chains that the Plasma bridge operates on are less user-friendly and can be less convenient to use.
Polygon Protocol
The Polygon network is powered by the Polygon Protocol, which consists of a set of smart contracts deployed on the Ethereum blockchain. The protocol is designed to offer a wide range of features to users, including but not limited to:
- Gas-free withdrawals. This feature allows users to withdraw their tokens from the Polygon network without having to pay gas fees.
- Fast transactions. Transactions on the Polygon network are confirmed in just a few seconds.
- Low transaction fees. Users only have to pay a small fee when they make a transaction on the network.
- Compatibility with multiple programming languages. This makes it much easier for developers to create and deploy dApps on the Polygon network.
How Does Polygon Differ from Other Blockchains?
Polygon has quite a few features that make it stand out from the crowd of many other cryptocurrencies and/or layer 2 solutions. Some of them we have already mentioned above — namely, its unprecedented interoperability with the Ethereum blockchain, low fees, high transaction speeds, support of multiple programming languages, and so on. However, that’s not all that makes it unique.
Most importantly, the combination of scaling solutions offered by Polygon is possibly complete like no other: in addition to the plasma chains and sidechains mentioned above, it also has zk (zero-knowledge) and optimistic rollups. Developers can pick whichever solution fits their project best, which makes the Polygon network incredibly flexible.
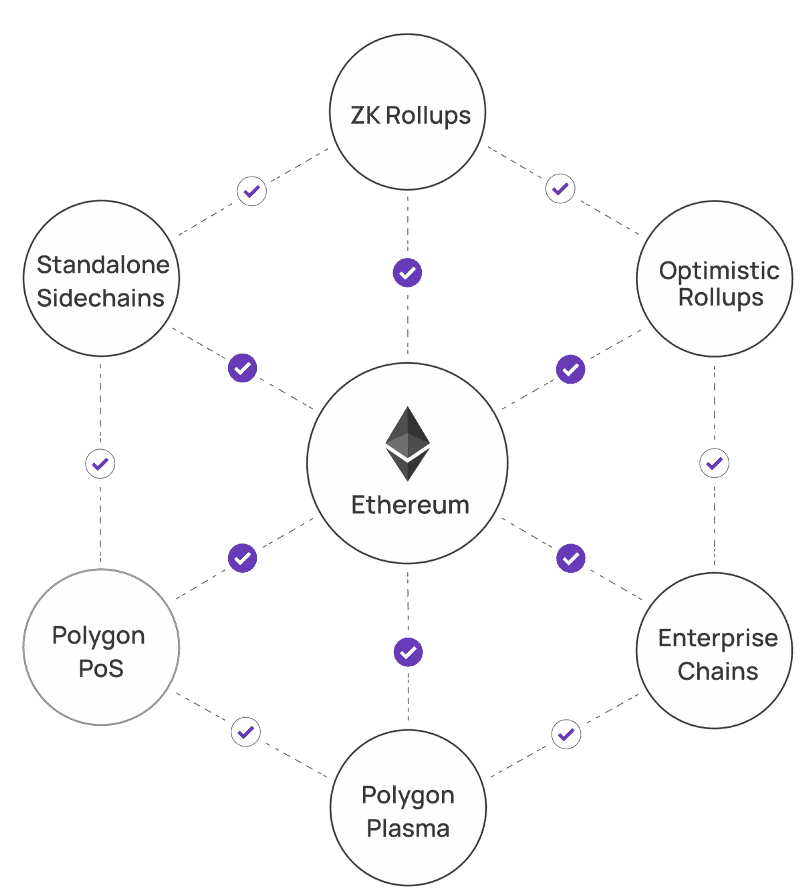
Polygon is also an EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) sidechain, but that doesn’t make the project unique in itself. However, it actually commits checkpoints to Ethereum, which significantly boosts the security of the whole network. That’s where the difference between Polygon and other EVM-compatible projects lies.
Polygon’s Software Development Kit (SDK)
The Polygon software development kit is what makes it easy for developers to build dApps on the network. As we have already mentioned above, its SDK supports a wide variety of different programming languages, which makes it accessible to a vast range of developers.
According to the development team, with this SDK, Polygon aims to transform Ethereum into a fully-fledged multi-chain system. Although many chains are already working on Ethereum, they are a bit chaotic: the Polygon SDK wants to introduce that much-needed structure to the ecosystem. This is done using two different types of solutions:
- Secured Chains – The Layer 2 solution
Secured chains are layer 2 solutions that rely on the main Ethereum chain for all their security needs instead of establishing their own validators. The SDK adds support for the most popular layer 2 solutions, such as zk-rollups or optimistic rollups. This part of the kit is perfect for both startups and more established projects that require a high level of security.
- Stand-Alone Chains
Stand-alone chains are blockchains that have their own security solutions and thus aren’t as dependent on the Ethereum main chain. These mostly include sidechains and various enterprise chains. They are less decentralized and not as secure as other solutions, but they offer more independence and flexibility, making them perfect for projects with strong communities and enterprises.
Polygon SDK Architecture
The architecture of the Polygon development kit was designed to provide maximum Ethereum compatibility, modularity, and extensibility. All of its elements support the main goals of the network. Here’s what it looks like:
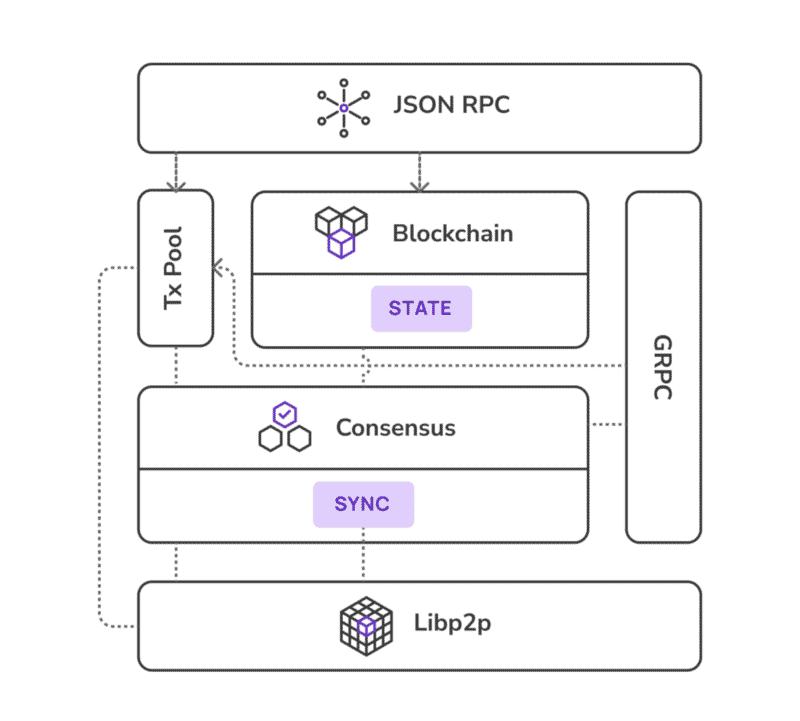
You can learn more about it in this article on Polygon’s blog.
Which DApps Does Polygon Use?
Polygon currently supports over 7,000 dApps, with more emerging every week. Some of the most popular Polygon-based decentralized applications include:
- Sunflower land, a game
- QuickSwap, an exchange
- Arc8, a game
- 1inch Network, a DeFi project
- Uniswap V3, an exchange
According to the website DappRadar, while games make up most projects with a high number of unique addresses, they still bring in a relatively small amount of profit and trading volume. Exchanges and DeFi projects are typically not as popular yet have a much higher amount of crypto being passed through the network’s smart contracts.
Final Thoughts
The Polygon project is already an incredibly innovative and efficient network and dApps deployment platform in its own right: the fact that it’s a scaling solution for Ethereum is just a bonus. The Ethereum-Polygon synergy attracts much attention to this project, but it also has fans that like it for what it is: a great platform for multi-chain solutions and dApp deployment.
Thanks to plenty of partnerships, including those with major companies, such as Disney and Coca-Cola, Polygon’s price increased by over 100% during a harsh bear market. Considering MATIC tokens can also be staked, it definitely became a very attractive cryptocurrency for all kinds of investors.
Overall, Polygon has a real chance of becoming one of the major solutions that help scale Ethereum and of being a widely adopted cryptocurrency that keeps on getting more mainstream. We are definitely excited about its further development!
FAQ
Is Polygon a good investment?
Polygon has a lot going for it and seems to be relatively future-proof. Ultimately, however, what defines it as a good investment or not is how it fits your portfolio.
What is the Polygon crypto used for?
Polygon is a layer 2 solution that increases scalability and reduces fees on the Ethereum network. It can also be used to deploy dApps and stake MATIC tokens.
Does the Polygon crypto have potential?
The crypto market is extremely unpredictable, but Polygon has a lot of things that can help a crypto asset book a one-way ticket to the moon: a big market cap, innovative functionality, prospects, and a great community.
Is Polygon the same as Ethereum?
While the two naturally have their similarities, Polygon and Ethereum are two different cryptocurrencies.
Disclaimer: Please note that the contents of this article are not financial or investing advice. The information provided in this article is the author’s opinion only and should not be considered as offering trading or investing recommendations. We do not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or regular crypto users should research multiple viewpoints and be familiar with all local regulations before committing to an investment.

